ARIMA模型(Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average model),差分整合移動平均自迴歸模型,又稱整合移動平均自回歸模型,利用這個模型可以對時間序列資料做預測分析,像是股票價格,營業銷售預測,今天就來預測 COVID-19 的疫情。
首先,前面幾篇已經談到如何將約翰·霍普金斯大學的疫情統計抓資料下來,程式碼:
library(tidyverse)
library(ggplot2)
library(cowplot)
library(patchwork)
library(forecast)
path <- "https://raw.githubusercontent.com/CSSEGISandData/COVID-19/master/csse_covid_19_data/csse_covid_19_time_series/"
confirm_file <- "time_series_covid19_confirmed_global.csv"
deaths_file <- "time_series_covid19_deaths_global.csv"
recovered_file <- "time_series_covid19_recovered_global.csv"
confirmed_df <- read_csv(paste0(path, confirm_file))
deaths_df <- read_csv(paste0(path, deaths_file))
recovered_df <- read_csv(paste0(path, recovered_file))
range <- 60
sd <- length(confirmed_df) - range; sd
ed <- length((confirmed_df)); ed
dates <- colnames(confirmed_df[, sd:ed]); dates
dates <- as.Date(dates,format = "%m/%d/%y"); dates
#date.list <- seq(from=as.Date(dates[1]),
# to=as.Date(dates[range+1]), by=1); date.list
getCountrydata <- function(Country,
dates = dates,
confirmed_df = confirmed_df,
deaths_df = deaths_df,
recovered_df = recovered_df,
sd = sd, ed = ed) {
if (Country == "all") {
cases <- confirmed_df %>%
#select(-(1:400)) %>%
select(sd:ed) %>%
colSums()
death <- deaths_df %>%
#select(-(1:400)) %>%
select(sd:ed) %>%
colSums()
recovered <- recovered_df %>%
#select(-(1:400)) %>%
select(sd:ed) %>%
colSums()
}
else {
Country <- enquo(Country)
cases <- confirmed_df %>%
filter(`Country/Region` == !! Country) %>%
#select(-(1:400)) %>%
select(sd:ed) %>%
colSums()
death <- deaths_df %>%
filter(`Country/Region` == !! Country) %>%
#select(-(1:400)) %>%
select(sd:ed) %>%
colSums()
recovered <- recovered_df %>%
filter(`Country/Region` == !! Country) %>%
#select(-(1:400)) %>%
select(sd:ed) %>%
colSums()
}
res.df <- tibble(dates,
cases = cases,
death = death,
recovery = recovered,
mortality_rate = death/cases,
recovery_rate = recovery/cases)
return(res.df)
}
world.df <- getCountrydata(Country = "all",
dates = dates,
confirmed_df = confirmed_df,
deaths_df = deaths_df,
recovered_df = recovered_df, sd, ed)
#Taiwan
taiwan.df <- getCountrydata(Country = "Taiwan*",
dates = dates,
confirmed_df = confirmed_df,
deaths_df = deaths_df,
recovered_df = recovered_df, sd, ed)
getdailycase <- function(comfirmed_df, new.df, country, sd, ed, dates) {
sd <- sd - 1
ed <- sd
dates <- colnames(confirmed_df[, sd:ed])
df <- getCountrydata(Country = country,
dates = dates,
confirmed_df = confirmed_df,
deaths_df = deaths_df,
recovered_df = recovered_df, sd, ed)
first_data <- df$cases[[1]] ; first_data
new.df['daily'] <- NA;
for(i in 1:nrow(new.df)) {
if(i == 1)
new.df$daily[i] <- new.df$cases[i]- first_data
else
new.df$daily[i] <- new.df$cases[i]- new.df$cases[i - 1]
}
new.df
}
taiwan.df <- getdailycase(confirmed_df, taiwan.df, "Taiwan*", sd, ed, dates)
我們取最近60天的資料來做分析,資料名稱為 taiwan.df,輸入tail(taiwan.df)可以看到最後6筆(天)的資料:
1.載入zoo 套件包,以便將資料轉成可視的時間序列
library(zoo)
2.將taiwan.df的 death (死亡組數欄位)依日期做成zoo.ts 時間序列
zoo.ts <- zoo(as.numeric(taiwan.df$death), dates)
3.自動ARIMA模型分析
arc <- auto.arima(zoo.ts)
summary(arc)

4.對分析後的數據 arc 預測4天後的資料存於 fc1
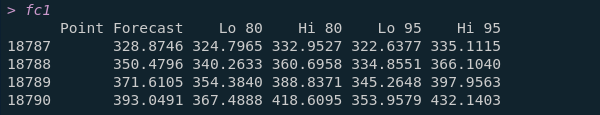
fc1 <- forecast(arc, h=4)
5.畫圖:
plot(fc1, xlab="Date", ylab="Comfirmed Cases")
我們可以看到預測往後四天死亡總人數最高最低的預測數字。
因為這圖是對時間序列來繪圖,因此要對這圖表的時間軸轉成日期的格式。
先把圖的x軸座標隱藏
plot(fc1, xaxt="n", xlab="Date", ylab="Death")
用函數 time() 將資料zoo.ts的日期取出存於tt
tt <- time(zoo.ts)
將這日期依間隔10天做成一個向量
ds.lst <- seq(1, length(tt), by=10)
日期格式變數為 YYYY-MM 的格式
fmt <- "%Y-%m"
依時間格式將日期轉成字串標籤
labs <- format(tt[ds.lst], fmt)
畫出X軸的格線
axis(side=1, at = tt[ds.lst], labels=F)
將日期用text函數補上去,角度45度,字體縮小0.8
text(x=tt[ds.lst], y=par()$usr[3]-15, labels=labs,
srt=45, adj=1, cex=0.8, xpd=TRUE)
下面是對每日確診數做7日的預測:
library(zoo)
zoo.ts <- zoo(as.numeric(taiwan.df$cases), dates)
arc <- auto.arima(zoo.ts)
summary(arc)
fc1 <- forecast(arc, h=7)
plot(fc1, xaxt="n", xlab="Date", ylab="Comfirmed Cases")
tt <- time(zoo.ts)
ds.lst <- seq(1, length(tt), by=10)
fmt <- "%Y-%m"
labs <- format(tt[ds.lst], fmt)
axis(side=1, at = tt[ds.lst], labels=F)
text(x=tt[ds.lst], y=par()$usr[3]-500, labels=labs,
srt=45, adj=1, cex=0.8, xpd=TRUE)
輸出結果:
可以看未來7日的每日確診數區間
80%最低11783~12016,80%最高12005~14183
95%最低11724~11442,95%最高12064~14757
您可以參考相關文章:










沒有留言:
張貼留言